General, quoting & support.
Add: Building E, No.58, Nanchang Road, Xixiang , Baoan District Shenzhen City, Guangdong, China
Tel : 0755-27348887
Fax : 0755-27349876
E-mail : svc@pcbastore.com
2021 Detail Guide for PCB Conformal Coating
Simon / 2021-04-02
Contents [hide]
In the past, conformal coatings could only be found in military and medical fields because they were expensive. With time, however, its usage is increasingly gaining popularity in other sectors due to affordable pricing, as a result of increased conformal coating technologies.
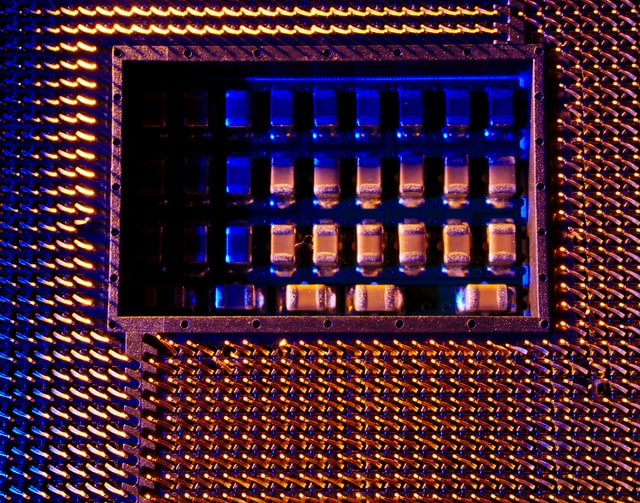
What are Conformal Coatings?
Conformal coating describes a non-conductive protective layer comprised of a material that protects circuit boards and electronic products from environmental erosion caused by moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. As the name suggests, the coating takes in the shape and standard of the circuit board components.
A conformal coating serves two purposes; it is a protective shield as well as an insulator for a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). It is thus suitable for use on boards that are often exposed to harsh environments.
Benefits of PCB Conformal Coating
-Insulation
Being a non-conductive layer, it acts as an insulator and reduces the spacing between conductors due to the increase of dielectric strength.
-Prevents erosion
PCB conformal coating acts as a barrier against possible contaminants like moisture, fungus, dust, and salt spray and hence preventing erosion.
-Protects against thermal and mechanical pressure
It offers protection against damage due to rough handling during installation by reducing mechanical and thermal stress.
-Enhances reliability
The coating helps in extending the shelf-life of circuit boards and other electronics hence improving their reliability.
-Double service
PCB conformal coating minimizes the need to install complex and complicated enclosures used to protect circuit boards.
-Light-weight
PCB conformal coating is a thin layer of protection; it, therefore, has an insignificant effect on the circuit board weight.
-High resistance
The conformal coatings are resistant to various kinds of solvents and chemicals and also heat.
Different Types of PCB Conformal Coating
Conformal coatings come in different types of materials depending on their specific application and usage. Coatings are categorized depending on their base resin. Discussed here are some of the commonly available conformal coating chemistry.
-Acrylic Resin (AR)
Popular due to their economical aspect, AR coatings are known to provide good protection against a wide range of contamination. They are advantageous in that they have a high level of dielectric strength and are easy to apply and repair making their application process less expensive. A major drawback pertains to their inability to protect against solvents and solvent vapors, making them unsuitable for aerospace applications.
-Silicone Resin (SR)
This type of coating is suitable in areas with high humidity. The fact about silicone resin is that it offers protection against a broad temperature range. It is resistant to many contaminants including chemicals, salt spray, and moisture. More so, it's very flexible and holds up well against vibration stress. On the downside, it offers no resistance to abrasion due to its rubbery nature, it's difficult to remove, has brush agitation, and takes longer to soak.
-Urethane Resin (UR)
UR is popularly known for its ideal moisture and chemical resistance. It shares most characteristics with silicone resin. For instance, both are abrasion and solvent resistant, a factor that makes their removal difficult. UR coatings are commonly used in aerospace applications for their excellent resistance to fuel vapors.
-Epoxy Resin (ER)
ER does not compare with other types of conformal coating. Its application is for the complete encapsulation of electronics. ER forms a solid layer that is permanent. It implies that when the coating cures, it cannot be removed. ER is the perfect form of protection against humidity, abrasion, and any form of chemical contamination.
Before any application of epoxy resin, protection measures must be made for fragile devices. The fact that it is a solid layer means it has the potential to offer high internal stress.
-Parylene Conformal Coating
This is a specialized conformal coating meant for vapor phase deposition. The advantage is that it provides good dielectric strength and is resistant to most contaminants including moisture, solvents, and harsh temperatures. In application, only a thin layer is required. The one disadvantage of parylene coating is that it is difficult to remove.
How to Apply PCB Conformal Coating
There are three major ways of applying conformal coating on your circuit boards.
-Dipping
This method of application is well suited for high-volume manufacturing. In this process, the boards are immersed in the conformal coating so that it penetrates throughout the board.
When using this method of application, perfect masking is required to minimize leakages. It is not a commonly used technique since most PCB board designs available in the market are not suitable for such an application.
-Brushing
This method is effective when done by an expert operator. Unlike dipping, brushing is suitable for low volume manufacturing. It is also ideal for repairing and finishing units of PCB boards.
-Spraying
This is the most commonly used technique. The application suits both low and high-volume manufacturing. This application can either be done manually or using a robotic system.
The robotic system of application is ideal and effective for it is easy to repeat and control the process. The system is only programmed and then it sprays the coating in the designed pattern of each board.
Different nozzles can be used in spraying. Fan spray nozzles are however recommended for someone seeking coverage for large areas or broad circuit boards. Precision needles are then used to provide cover around the edges and bases.
Manual spraying on the other hand is ideal for boards that are fairly flat and with components of almost the same height. Unlike robot spraying, this kind of application is tedious and uncontrolled. It, therefore, needs to be done by a highly skilled individual for you to achieve a consistent and even coating.
In a case the board is not coated all around, masking has to be done before spraying and later removed, a process that is quite time-consuming and increases labor costs.
Boards require curing after a conformal coating is applied. It can either be by air drying, oven drying, or by the use of UV light. The final product of this process is often a thin layer of a clear and shiny material of different textures.
Considerations to make when determining a conformal coating application process include:
Production requirement- the coating process is significantly impacted by the production method. This is in form of the preparation needed as well the coating process speed.
Circuit board design- the kind of board and its components affect that coating process. A board with many connectors and solvent and moisture sensitive components impacts the whole process.
Equipment needed- depends on the kind of coating you want to achieve. For example, specialized equipment might not be needed for a sporadically coated circuit.
Quality requirement- for coatings that are mission-related like military and aerospace, a high-quality coating is desired. It, therefore, means robotic spray application is needed to achieve a reliable and consistent coating.
How to remove PCB conformal coating
Method of removal depends on the material used. Some will require chemical solvents while others abrasion and mechanical techniques. Some of the methods of removal include;
Chemical solvent method
This method is effective in removing urethane, acrylic and silicone PCB conformal coating.
Peeling method
The coat is peeled using a blunt knife or blade. It is effective for removing silicone and any other thick rubber coating.
Thermal method
As the name suggests, the process involves the use of heat. Low-temperature heat is used to melt the coating gently.
The Common Conformal Coating Defects
Many issues arise with conformal coating application due to the various variables consisted in the coating process. Here are some of the common conforming coating defects, potential causes, and how to solve them.
De-wetting
This defect can be detected by an uneven coat on the surface. The common cause of de-wetting is the contamination of incompatible substrate either through the handling process or manufacturing.
Before making any conforming coating application, it is recommended that you thoroughly clean the substrate.
Capillary Flow
With this defect, the coating tends to flow away from one part of the substrate to the other. This defect develops during the drying and curing process. Capillary flow can be noticed by the presence of uncoated areas, uneven finish, and patches.
The common causes of capillary flow are low viscosity and high surface tension of the coating material, uneven or high amount of coating applied, and even low surface energy of the substrate.
Before any application, ensure the substrate is clean, reduce coating thickness and consider using the solvent-based coating. For the coating to dry fast, consider heating the board before making an application.
Cracking or Crazing
This is witnessed by the presence of coating fractures on a smooth surface. The small cracks are referred to as crazing. Cracking is often caused by using very thick film and inadequate time between overcoats. In some other cases, it can be caused during the curing process when excessive high temperature is used.
During the curing process, it is advised that you give the coating time to dry. This means you use lower temperatures for a longer period. It is also important that you apply a recommended coating thickness.
Delamination
Delamination is characterized by the presence of an exposed area below a coating. This occurs when the coat lifts away from the substrate. The common causes of delamination include the presence of contaminants on the surface, incompatibility of the coating and substrate as well as inappropriate coating.
To prevent delamination, clean the surface well before coating and use a recommended or specified coating thickness. You could also consider using natural evaporation, without forcing the coating to dry.
Orange peel
As the name suggests, an orange peel is characterized by an uneven mottled look.
The texture and appearance are comparable to orange skin. There are many causes including improper application, inadequate coating, and insufficient curing time.
Conclusion
Conformal coating for PCB is essential and important when the application is done appropriately. The best way to avoid defects and have the perfect coating is to consider an experienced technician.







